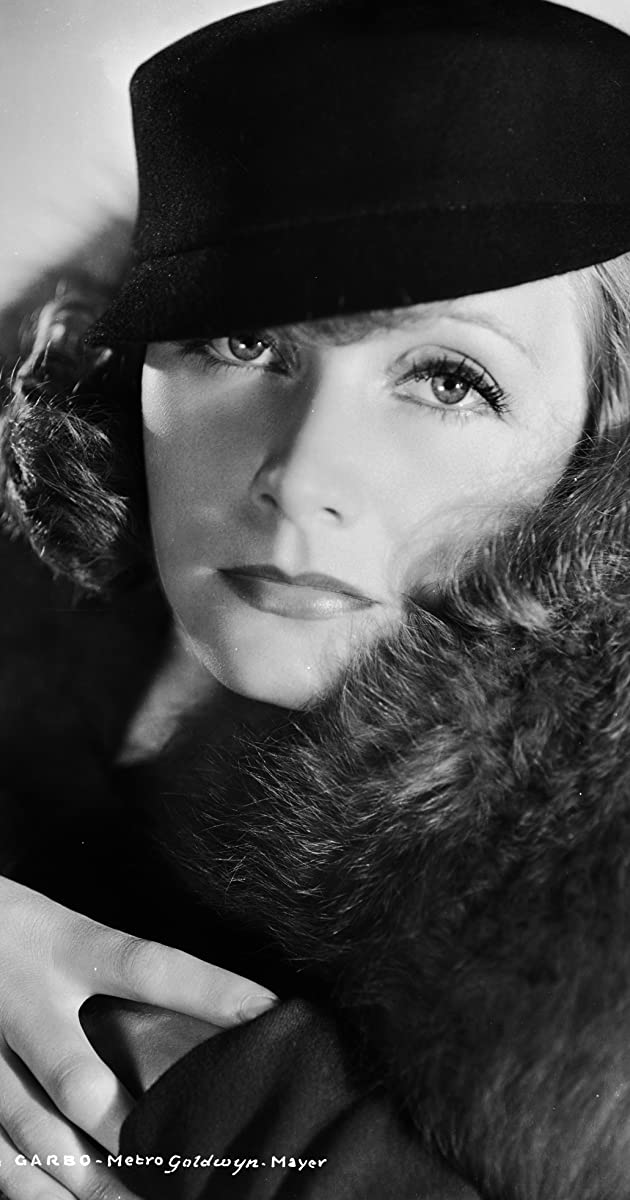
Greta Garbo was born Greta Lovisa Gustafsson on September 18, 1905, in Stockholm, Sweden, to Anna Lovisa (Johansdotter), who worked at a jam factory, and Karl Alfred Gustafsson, a laborer. She was fourteen when her father died, which left the family destitute. Greta was forced to leave school and go to work in a department store. The store used her as a model in its newspaper ads. She had no film aspirations until she appeared in short advertising film at that same department store while she was still a teenager. Erik A. Petschler, a comedy director, saw the film and gave her a small part in his Luffar-Petter (1922). Encouraged by her own performance, she applied for and won a scholarship to a Swedish drama school. While there she appeared in at least one film, En lyckoriddare (1921). Both were small parts, but it was a start. Finally famed Swedish director Mauritz Stiller pulled her from the drama school for the lead role in Gösta Berlings saga (1924). At 18 Greta was on a roll.
Following Joyless Street (1925) both Greta and Stiller were offered contracts with MGM, and her first film for the studio was the American-made Torrent (1926), a silent film in which she didn’t have to speak a word of English. After a few more films, including The Temptress (1926), Anna Karenina (1927) and A Woman of Affairs (1928), Greta starred in Anna Christie (1930) (her first “talkie”), which not only gave her a powerful screen presence but also garnered her an Academy Award nomination as Best Actress (she didn’t win). Later that year she filmed Romance (1930), which was somewhat of a letdown, but she bounced back in 1931, landing another lead role in Mata Hari (1931), which turned out to be a major hit.
Greta continued to give intense performances in whatever was handed her. The next year she was cast in what turned out to be yet another hit, Grand Hotel (1932). However, it was in MGM’s Anna Karenina (1935) that she gave what some consider the performance of her life. She was absolutely breathtaking in the role as a woman torn between two lovers and her son. Shortly afterwards, she starred in the historical drama Queen Christina (1933) playing the title character to great acclaim. She earned an Oscar nomination for her role in the romantic drama Camille (1936), again playing the title character. Her career suffered a setback the following year in Marie Walewska (1937), which was a box office disaster. She later made a comeback when she starred in Ninotchka (1939), which showcased her comedic side. It wasn’t until two years later she made what was to be her last film, Two-Faced Woman (1941), another comedy. But the film drew controversy and was condemned by the Catholic Church and other groups and was a box office failure, which left Garbo shaken.
After World War II Greta, by her own admission, felt that the world had changed perhaps forever and she retired, never again to face the camera. She would work for the rest of her life to perpetuate the Garbo mystique. Her films, she felt, had their proper place in history and would gain in value. She abandoned Hollywood and moved to New York City. She would jet-set with some of the world’s best-known personalities such as Aristotle Onassis and others. She spent time gardening and raising flowers and vegetables. In 1954 Greta was given a special Oscar for past unforgettable performances. She even penned her biography in 1990.
On April 15, 1990, Greta died of natural causes in New York and with her went the “Garbo Mystique”. She was 84.